- About Vanuatu
The Republic of Vanuatu is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago is located some 1,750km east of Australia, 500km north-east of New Caledonia, west of Fiji and south of the Solomon Islands. Vanuatu is only 2.5 hours flying time north-east of Brisbane and 3.5 hours from Sydney, Australia. It’s a little over 2 hours from Auckland, New Zealand. There are regular flights from New Zealand, Honiara, Australia, Noumea and Fiji.
Full Name: Republic of Vanuatu
Capital City: Port Vila (on the island of Efate)
Area: 860,000 sq km, 332,046 sq miles Population: 301,695 (2020 NPHC VNSO)
Time Zone: GMT/UTC +11 ()
Languages: Bislama (official), French (official), English (official)
Religion: Christian (84%), animist (16%)
Currency: Vatu (VT)
Electricity: 230V 50HzHz
Electric Plug Details: Three Pin (Flat)
Country Dialing Code: +678
History
The first settlers to arrive in Vanuatu are believed to have arrived by canoe approximately 3,500 years ago from New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.
In 1606, the Portuguese explorer, Pedro Fernández de Quirós, discovered the island of Espiritu Santo, which he thought was a great southern continent believing it to be part of Terra Australis. Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that lasted until independence.
In 1887, the islands began to be administered by a French-British naval commission. In 1906, the French and British agreed to an Anglo-French Condominium (Joint Administration) on the New Hebrides. During World War II, the islands of Efate and Espiritu Santo were used as allied military bases. In the 1960s, the Ni-Vanuatu people started to press for self-governance and later independence; full sovereignty was finally granted by both European nations on July 30, 1980. After independence, Vanuatu joined the UN in 1981, and the Non-Aligned Movement in 1983.
Politics
The parliament of Vanuatu is unicameral in that it has one single decision making body, of which comprises 52 members whom are duly elected every four years by popular vote. The leader of the main party in the parliament is usually elected Prime Minister, and heads the government. The head of state, the President, is chosen every five years by the parliament and the presidents of the six provincial governments.
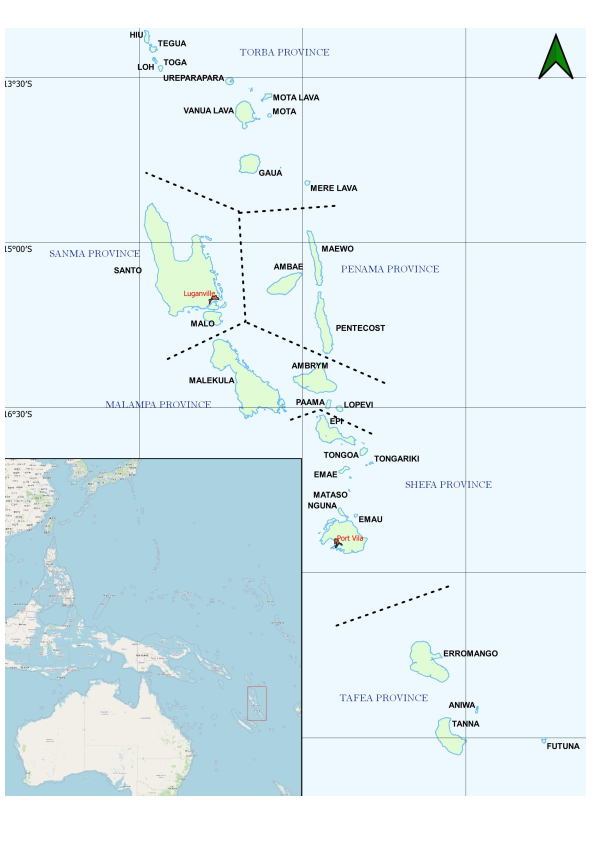
Provinces
Since 1994, Vanuatu has been divided into the six provinces of Malampa, Penama, Sanma, Shefa, Tafea and Torba. The main Islands within these provinces include: Banks and Torres (Torba), Espiritu Santo (Sanma), Maewo and Pentecost (Penama), Malekula, Ambrym (Malampa), Epi, Efate (Shefa), Erromango, Tanna and Aneityum (Tafea)
Geography
Vanuatu is an archipelago of 83 islands, of which two — Matthew and Hunter — are also claimed by the French overseas department of New Caledonia. Of all the 83 islands, 14 have surface areas of more than 100 square kilometers, from largest to smallest: Espiritu Santo (3956 km), Malakula (2041 km), Éfaté (900 km), Erromango (888 km), Ambrym (678 km), Tanna (555 km), Pentecôte (491 km), Épi (445 km), Ambae or Aoba (402 km), Vanua Lava (334 km), Santa Maria (328 km), Maéwo (304 km), Malo (180 km) and Anatom or Aneityum (159 km). Most of the islands are mountainous and of volcanic origin, and have a tropical or sub-tropical climate. The nation’s largest towns are the capital Port Vila, which is situated on Efate, and Luganville, on Espiritu Santo. The highest point in Vanuatu is Mount Tabwemasana, at 1879 m (6158 ft), on the island of Espiritu Santo. There are several active volcanoes in Vanuatu, including Yasur on the island of Tanna, one of the world’s most accessible volcanoes, as well as several underwater ones.
Ecology
Vanuatu is recognized as a distinct terrestrial ecoregion, known as the Vanuatu rain forests. Vanuatu is part of the Australasia ecozone, which also includes neighboring New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands, as well as Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
Economy
The economy is based primarily on subsistence or small-scale agriculture, which provides a living for 65% of the population. Fishing, offshore financial services, and tourism (with about 60,000 visitors in 2005), are other mainstays of the economy. Mineral deposits are negligible; the country has no known petroleum deposits. A small light industry sector caters to the local market. Tax revenues come mainly from import duties and a 12.5 percent Value Added Tax (VAT) on goods and services.
Demographics
Vanuatu has a population of 301,695 (2020 NPHC VNSO). Most of the population is rural, though Port Vila and Luganville have populations in the tens of thousands. Most of the inhabitants of Vanuatu (98.5%) are native Melanesian, or Ni-Vanuatu, with the remainder made up of a mix of Europeans, Asians and other Pacific islanders. A few of the islands are Polynesian outliers. About 2,000 Ni-Vanuatu live and work on New Caledonia.
Information sourced from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vanuatu (with editing by the VTO), Vanuatu Tourism Office Government of Vanuatu)


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt